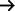- 13-Feb-23
The hallmark symptoms of mumps include painful, swollen jaws and puffed-up cheeks. This is a result of parotitis which is characterised by swollen salivary glands under the ears on one or both sides. A few days prior to parotitis, other symptoms that could appear include Fever and Headaches.
What are Mumps?
The salivary glands are the main organs affected by the infectious viral infection known as mumps (Kaan Paray). Fever, headaches, aches in the muscles and sensitive, swollen salivary glands under the ear or in the jaw on one or both sides of the face are among the symptoms.
Mumps meaning in Urdu:
کن پھیڑ- یہ ایک وائرل انفیکشن ہے جو بنیادی طور پر کانوں کے قریب تھوک کے غدود کو نشانہ بناتا ہے۔ ممپس کی وجہ سے ایک یا دونوں غدود سوجن ہو سکتے ہیں۔ پہلے بڑے پیمانے پر، ممپس اب ویکسین کی بدولت بہت کم عام ہے۔ کھانسنے، چھینکنے اور کھانے کے آلات کے استعمال سے ممپس ایک متاثرہ شخص سے دوسروں میں پھیل سکتا ہے۔
Mumps in Children:
A child with the highly contagious viral illness known as the mumps typically experiences a fever and enlarged salivary glands in his mouth and vicinity of his ear. There may also be a role for the central nervous system.
-
From child to child, it spreads.
-
Before symptoms show, children are contagious for one to seven days.
-
To aid in illness prevention, a vaccine is accessible.
-
Being viral, there is no treatment for it, but it is manageable.
-
Early symptom relief aids in avoiding major consequences.
Causes of Mumps:
The mumps virus, which is a member of the paramyxovirus family, is what causes mumps. The virus primarily spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes or by direct contact with an infected person's saliva. When a person is exposed to the virus, it infects the salivary glands and other parts of the body causing inflammation and symptoms such as fever, headache and swollen and tender salivary glands.
People who are not vaccinated against mumps or who did not develop immunity to the virus after having the disease are at a higher risk of contracting mumps. Other factors that can increase the risk of contracting mumps include being in close proximity with infected individuals such as attending the same school or living in the same household and having a weakened immune system due to other health conditions or medications.
Mumps Symptoms:
The symptoms of mumps typically appear 16-18 days after a person is infected with the virus. Salivary glands under the ear or in the jaw on one or both sides of the face that are swollen and sensitive. This is the most characteristic symptom of mumps and is often referred to as "parotitis". The most common symptoms include:
-
Fever: A mild to moderate fever is common with mumps.
-
Headache: Many people with mumps experience a headache as well.
-
Muscle aches: Some people may feel achy or fatigued during the infection.
-
Loss of appetite: Some people may lose their appetite during the infection.
-
Fatigue: some people may feel weak or tired.
These symptoms usually last for about a week. In some cases, people with mumps may not have any symptoms but are still able to spread the virus to others. As mentioned before, mumps can also cause more serious complications such as inflammation of the testicles, ovaries, pancreas, brain, spinal cord and hearing loss but these are relatively rare. If you suspect that you or someone you know has mumps, it's important to seek medical attention.
Mumps Complications:
Mumps complications are more common in those who haven't received the vaccine. Even if a person's salivary glands weren't swollen, they could nonetheless occur. When the virus spreads to other body tissues, complications occur. Possible complications include:
Swollen testicles: This condition, commonly known as orchitis, produces excruciating discomfort. Mumps infections are more frequent after puberty. A bloated testicle may cause the size of the testicle to shrink, which could affect fertility.
Swollen ovaries: This consequence, which is also brought on by oophoritis, results in discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and fever. After puberty, this issue becomes more probable. Fertility does not appear to be impacted by the illness.
Encephalitis: Encephalitis is an inflammation-related swelling of the brain that may cause tissue damage. Changes in awareness, seizures, and loss of muscle control can all be results of this condition.
Meningitis: The swelling or inflammation of the membranes around the brain and spinal cord is known as meningitis. It could result in headaches, fever, and stiff neck. Mumps-related meningitis infrequently results in persistent issues.
Hearing loss: This problem may develop gradually or suddenly. Usually, hearing returns to normal following the sickness.
Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis, often known as pancreas injury from swelling, can result from mumps. Affected individuals may have stomach pain or tenderness, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Miscarriage: The risk of miscarriage, or the termination of a pregnancy, may rise if you contract the mumps in the first 12 weeks of your pregnancy.
When to see a Doctor?
If you or your child exhibits mumps symptoms, consult a medical professional. Following the onset of swelling for around five days, mumps can spread very quickly. Integrated Medical Care Hospital (IMC Hospital) is a reputable institution and is often termed one of the best hospitals in Pakistan. Here you find one of the Best Paediatrics (Child Specialists) in Lahore Pakistan. Visit today and book your appointment at Integrated Medical Care Hospital (IMC Hospital).
Dr. Muhammad Tauseef
MBBS, FCPS (Paediatrics, Pk), Clinical Fellow in Neonatology.
Specialities: Neonatology & Paediatrics.
Areas Of Focus: Neonatology (Medicine of newborn babies up to 28 days of life).
Dr. Sadaf Faisal Bhatti
MBBS, MRCP (UK), MD (USA), Diplomate American Board of Internal Medicine.
Specialities: Internal Medicine.
Areas Of Focus: Diagnostic dilemmas, Acute medical conditions, Women's Health and Wellness, Preventive Medicine and chronic illnesses (Obesity, Diabetes, HTN), seasonal allergies and Acute Bacterial and viral illnesses, Hepatitis, and High-level inpatient care.

 Map
Map